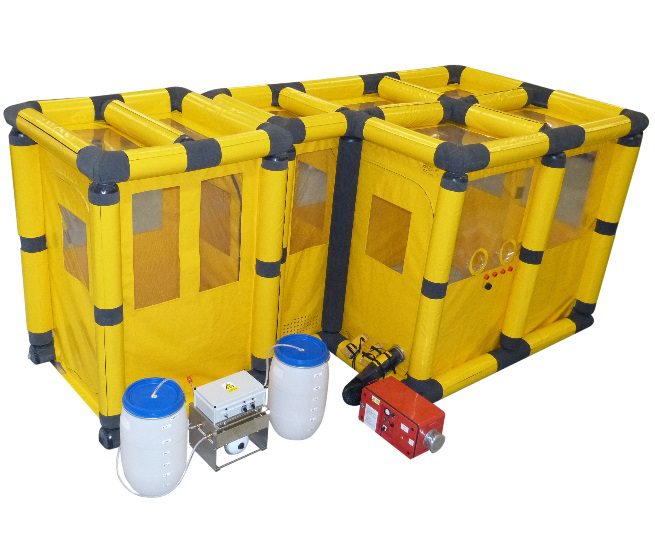
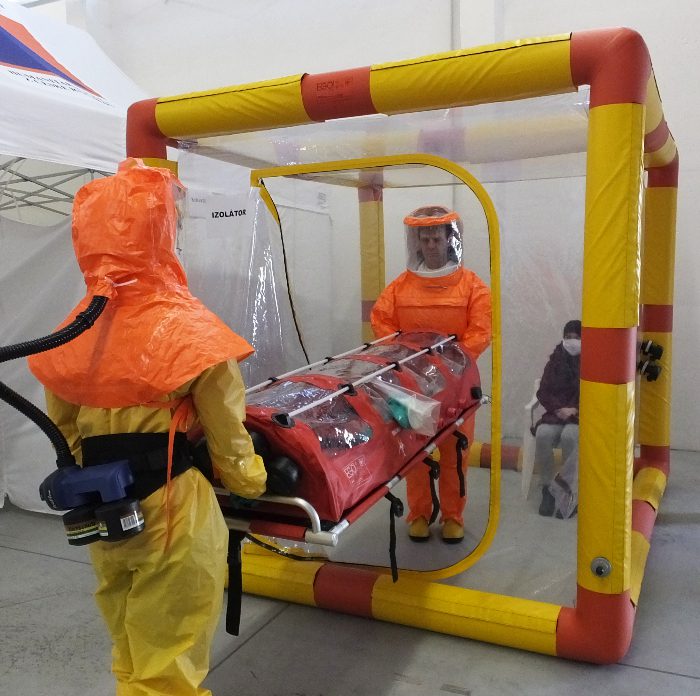
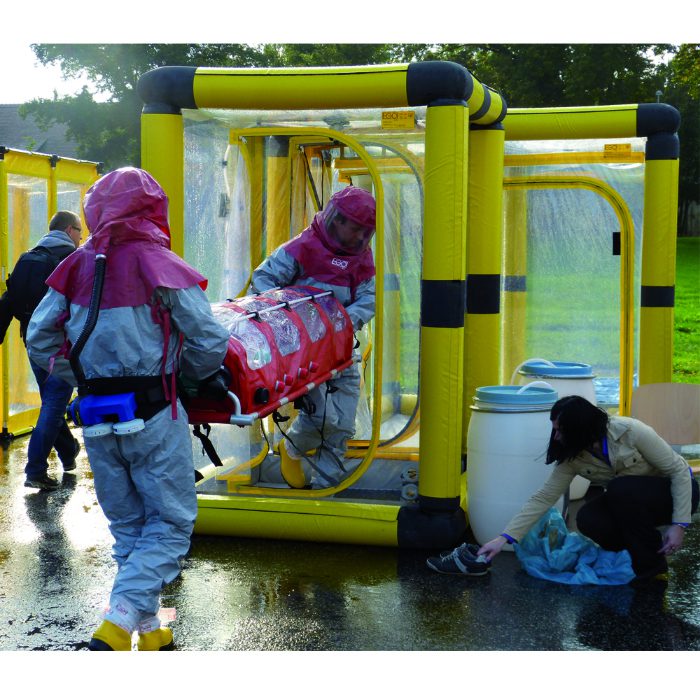
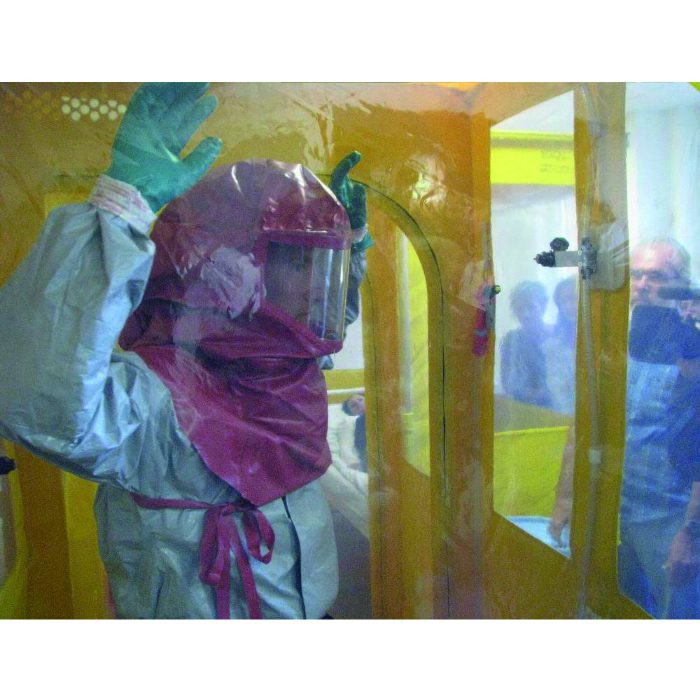
Description
Currently, we observe large migration flows of population especially in the context of local wars and civil wars, persecution or poverty. This migration affects also countries with less developed infrastructure and health care, where protection against highly virulent infections almost does not exist.
In the past, people were repeatedly attacked by various illnesses, for example plague, typhoid, cholera, malaria, which some of them still trouble the population and it is very difficult if not impossible to eradicate these diseases. Also, over the years it leads to the appearance of new and highly dangerous diseases threatening the whole continents. The evidence of that are facts of World Health Organization regarding the occurrence of highly infectious diseases such Ebola (more than 60 %), MERS-CoV (more than 30 %) or even the CVOID-19. Highly infectious diseases do not know the borders and if we are not prepared (as even the developed countries have experienced it as well), these infectious diseases can cause the panic which can paralyze the health care system with incalculable consequences. It is also necessary to take into consideration terrorist attacks, which means significant threat to the population and it is necessary to count that they may also include weapons of mass destruction, including biological agents.
In summary, in case of insufficient protection of the population and medical personnel can the situation with the occurrence of dangerous infection occur until stage of epidemics or pandemics. Creating an effective system for fast response requires vigilance, implementation of methodology and training and proper cooperation of crisis management such as hospitals, local and state health authorities, security forces, including the government forces.